18mm proximity sensor
- time:2024-11-08 01:34:02
- Click:0

Title: Unveiling the World of 18mm Proximity Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
In the vast landscape of sensor technology, one component stands out for its precision and versatility—the 18mm proximity sensor. This unassuming device plays a critical role in automation, safety monitoring, and beyond, making it an integral part of modern industrial applications and consumer electronics. Let’s delve into what makes these sensors unique and how they contribute to various technological advancements.
The Anatomy of an 18mm Proximity Sensor
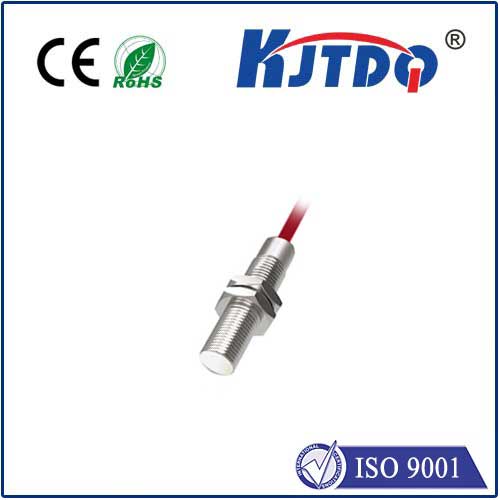
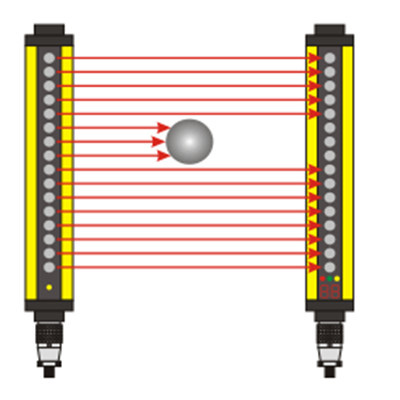
An 18mm proximity sensor is a type of sensor that detects the presence or absence of an object without physical contact. The “18mm” refers to the diameter of the sensor, which can vary depending on the specific application requirements. These sensors typically utilize electromagnetic fields, capacitive coupling, or optical means to sense nearby objects.
How Do 18mm Proximity Sensors Work?
There are three primary types of 18mm proximity sensors based on their operating principles:
- Inductive Proximity Sensors: These sensors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They generate an electromagnetic field that changes when a conductive object comes within range, triggering a signal output. Inductive sensors are ideal for metallic targets and are often used in industrial automation for tasks such as position detection, count monitoring, or speed measurement.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors: Capacitive sensors detect changes in the electrical field caused by the proximity of an object, whether it’s metallic or non-metallic. They are highly versatile and commonly employed in environments where hygiene and sensitivity are crucial, like food processing or medical equipment. Their ability to function even in dirty or dusty conditions makes them robust and reliable.
- Photoelectric Proximity Sensors: Also known as optical sensors, photoelectric models use light to detect objects. When an object interrupts or reflects a beam of light emitted by the sensor, it generates a signal. These sensors are useful for detecting transparent or semi-transparent materials, as well as in applications requiring high precision.
Applications Across Industries
The adaptability of 18mm proximity sensors makes them invaluable across multiple sectors. Here are some notable examples:
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing plants, they monitor conveyor belt movement, control robotic arms, or ensure machinery safety by detecting foreign objects in critical zones.
- Transportation Systems: From ensuring doors close properly on escalators to controlling traffic lights, proximity sensors enhance safety and efficiency.
- Consumer Electronics: They find their way into devices like smartphones (screen wake/sleep), smart appliances (door open/close detection), and automotive systems (parking assistance).
Conclusion: The Future is Proximity Sensing
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of proximity sensors. The 18mm variant, with its compact size and diverse functionality, exemplifies how sensor technology can seamlessly integrate into our daily lives, enhancing convenience, safety, and productivity. By understanding the fundamentals and applications of these sensors, we gain insight into the intricate web of technology that powers the modern world. Whether you’re an engineer designing the next big gadget or simply curious about the tech behind everyday objects, 18mm proximity sensors represent just one piece of the fascinating puzzle that is modern sensing technology.