check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
Title: Understanding the Different Types of Photo Eye Sensors
As technology continues to advance, photo eye sensors have become an integral part of various industries. From manufacturing to transportation, these sensors play a crucial role in detecting objects and measuring distances. In this article, we will explore the different types of photo eye sensors available on the market today.
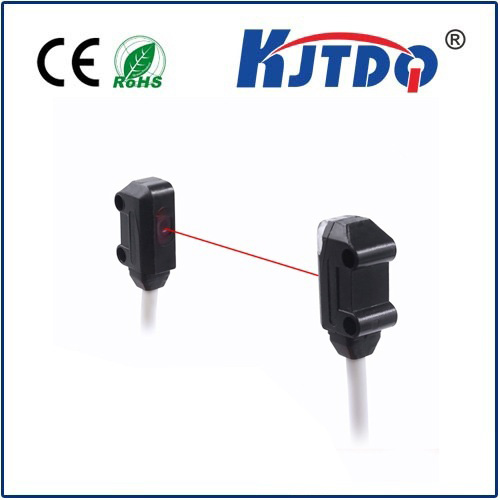
1. Through-Beam Sensors
Through-beam sensors are one of the most common types of photo eye sensors. They consist of two components: a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits a beam of light that is received by the receiver when there is no obstruction in its path. When an object passes through the beam, it interrupts the signal, triggering an output response from the sensor. These sensors are highly reliable and can detect objects at varying distances, making them ideal for applications such as packaging machines and conveyor systems.

2. Diffuse Sensors
Diffuse sensors, also known as reflective sensors, use a single component to both emit and receive light. They operate by projecting a beam of light onto an object and measuring the amount of light reflected back to the sensor. This type of sensor is best suited for detecting objects with varying surface materials and textures, as well as for applications where the distance between the sensor and the target is relatively short. Common uses for diffuse sensors include sorting machines and quality control inspections.
3. Color Sensors
Color sensors are designed to detect the color or spectral characteristics of an object. They are commonly used in printing and packaging industries to ensure color consistency and accuracy. These sensors work by analyzing the light reflected off an object's surface and comparing it to pre-set color references. Color sensors can be programmed to identify specific colors or shades, making them highly versatile in their applications.
4. Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors, also known as non-contact sensors, are designed to detect the presence of an object without physically touching it. They use electromagnetic fields or ultrasonic waves to detect objects within a certain range. Proximity sensors are commonly used in industrial automation and robotics applications, where they can provide accurate positioning and alignment information for machinery and equipment.
5. Fiber Optic Sensors
Fiber optic sensors utilize optical fibers to detect changes in light intensity, color, or polarization patterns. They are highly sensitive and can be used for various applications, including temperature monitoring, pressure sensing, and strain measurement. Fiber optic sensors are ideal for harsh environments or situations where electrical interference could be an issue due to their immunity to electromagnetic fields.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of photo eye sensors is essential for selecting the appropriate sensor for your specific application. Each type has its unique features and benefits, making them suitable for different industries and purposes. By considering factors such as detection distance, object size, material properties, and environmental conditions, you can choose the right photo eye sensor to improve efficiency and productivity in your operations.