check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
The advancement of automotive technology has been marked by a significant emphasis on sensor systems, with displacement, position, and proximity sensors being at the forefront of this transformation. In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between these sensors, their role in enhancing vehicle performance and safety, and the evolving significance of their applications in the automotive industry.
Displacement Sensors: Unleashing the Power Potential of Engines
The displacement sensor is responsible for providing real-time information about the engine's internal volume, which is crucial in determining how much fuel can be injected and how quickly it can be ignited. This sensor helps optimize the combustion process, leading to better fuel efficiency, increased power output, and reduced emissions. As automotive engineers continue to seek ways to enhance engine performance while minimizing fuel consumption and environmental impact, displacement sensors are playing an increasingly vital role.
Position Sensors: Enhancing Stability and Control during Acceleration and Deceleration
Position sensors are designed to measure the relative position of components within a vehicle's suspension system. They provide valuable data on the status of each link or joint in the suspension, allowing for more accurate control of the vehicle's movement during acceleration and deceleration. This information enables engineers to make informed decisions about how to optimize the suspension's performance, leading to improved stability, handling, and ride quality. As tire size and suspension design continue to evolve, position sensors will remain critical in ensuring that vehicles maintain optimal performance characteristics.
Proximity Sensors: Safeguarding Against Collisions and other Hazards
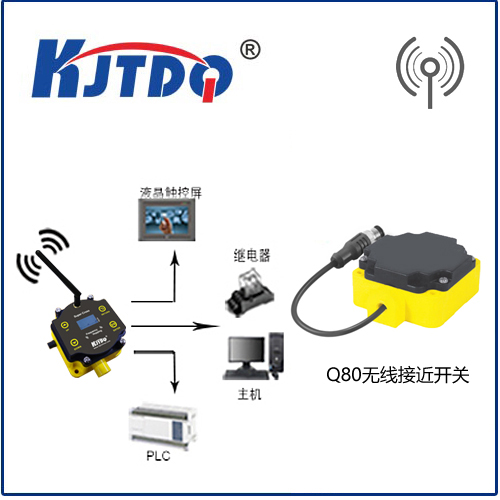
Proximity sensors are responsible for detecting the presence of objects or hazards in the vehicle's path. These sensors are particularly useful in collision avoidance systems, as they can alert drivers to potential hazards before they become dangerous situations. Additionally, proximity sensors can be used to monitor the position of pedestrians, cyclists, or other road users, helping to improve traffic flow and reduce accidents caused by human error. As autonomous driving technology continues to advance, proximity sensors will likely play an even more critical role in safeguarding passengers and other road users.
Conclusion: Achieving Enhanced Performance and Safety through Advanced Sensor Integration
The integration of displacement, position, and proximity sensors has revolutionized automotive technology by enabling more efficient engines, improved stability and control during acceleration and deceleration, and enhanced safety features such as collision avoidance systems. As these sensors continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the future of automotive engineering looks bright indeed. By leveraging the power of advanced sensor technology, automotive manufacturers can deliver vehicles that are not only safer but also more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient.