check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
Abstract: The demand for precision and efficiency in industrial applications has led to the development of innovative sensor technologies, among which non-contact (NC) proximity sensors stand out. In this article, we explore the advantages and features of no NC proximity sensors and how they can revolutionize various industrial processes. We also discuss their potential applications in fields such as manufacturing, robotics, and automation.
I. Introduction
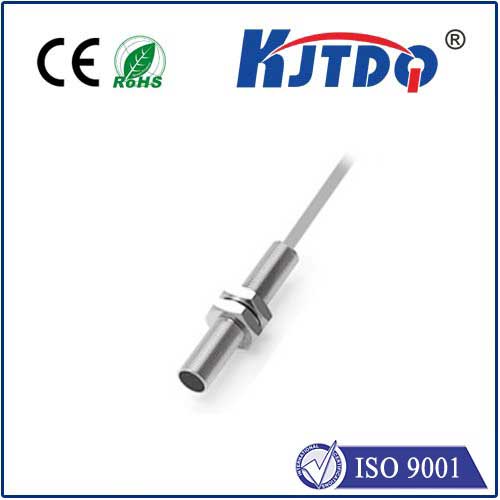
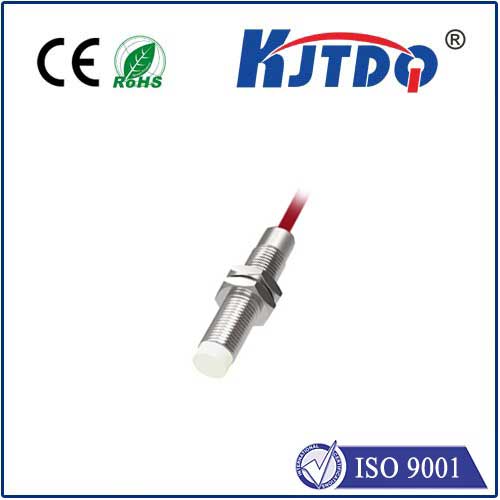
A. Overview of no NC proximity sensors
B. Importance of accurate and efficient industrial processes
C. The need for innovative sensor technologies
II. Advantages of No NC Proximity Sensors
A. Non-contact detection mechanism
1. Improved safety compared to traditional contact sensors
2. Reduced maintenance requirements
B. High accuracy and sensitivity
1. Continuously updating data without interruptions
2. Ability to detect small distances and angles
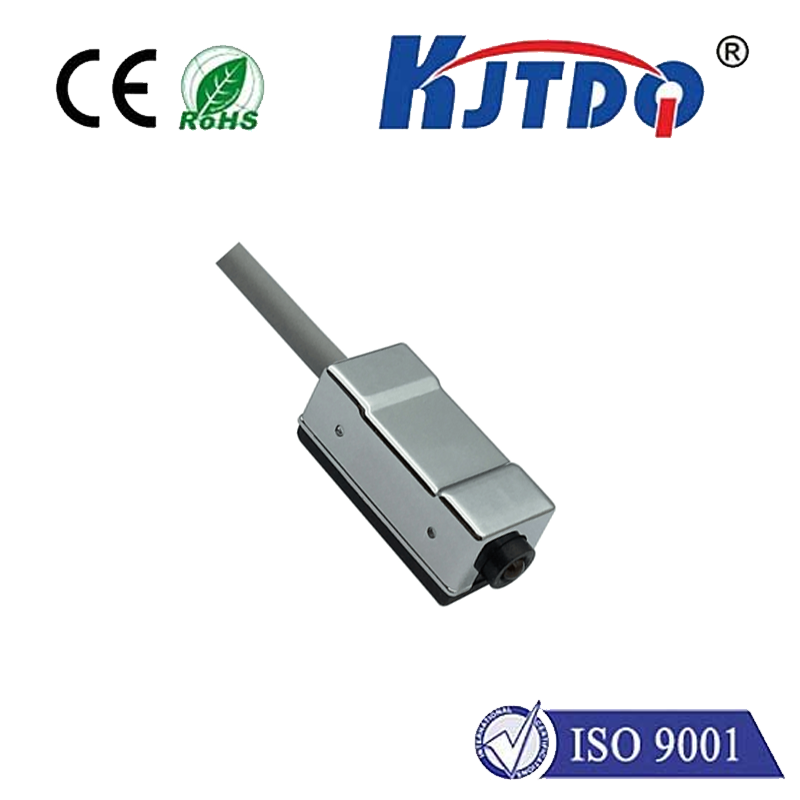
C. Versatility in application scenarios
1. Various industries served, such as manufacturing, packaging, and healthcare
2. Integration with existing systems and devices
D. Cost-effective solution for improved efficiency and productivity
III. Functionality of No NC Proximity Sensors
A. Detection modes and parameters
1. Ping mode: continuous monitoring of distance changes
2. Rfid mode: identification and tracking of objects or personnel
B. Data transmission and processing
1. Real-time data update and analysis
2. Integration with software for easy control and management of sensor networks
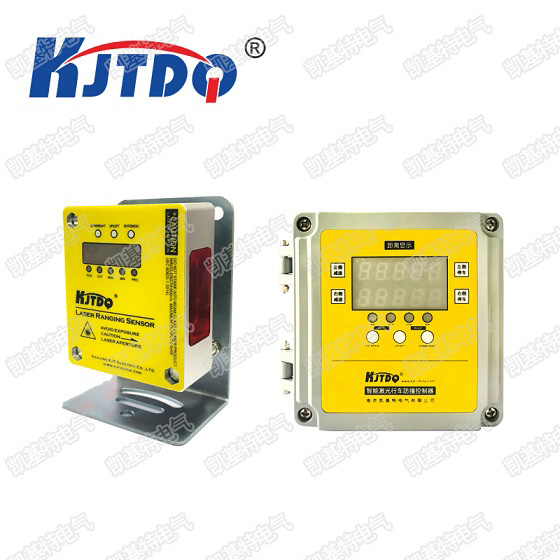
C. Operating conditions and environmental robustness
1. Sensitivity to different light sources and background noise levels
2. Ability to operate in harsh environments, such as high temperatures or extreme humidity
D. Energy efficiency and long battery life
1. Low power consumption compared to other types of sensors
2. Longevity and reliability due to advanced design and manufacturing processes
IV. Application Examples in Industrial Processes
A. Manufacturing: Assembly line optimization, quality control, and asset tracking
B. Robotics: Navigation, obstacle detection, and collaboration with humans
C. Automation: Inventory management, material handling, and safety monitoring in hazardous environments
D. Healthcare: Patient monitoring, equipment calibration, and remote access for medical professionals
V. Conclusion
A. Recap of the benefits of no NC proximity sensors in industrial applications
B. Future developments in sensor technology and its potential impact on industry growth and sustainability