check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
Metallurgy is an industry that demands high levels of precision, reliability, and safety. One of the key challenges faced by metallurgists is the detection of metals within the production process, especially when dealing with hazardous materials or large quantities of metals. Traditional methods of metal detection, such as magnetic sensors andX射线荧光分析(XRF), have limitations in terms of accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness. However, the advent of proximity sensors has revolutionized the way metal detectors are designed and used in the metallurgical industry.
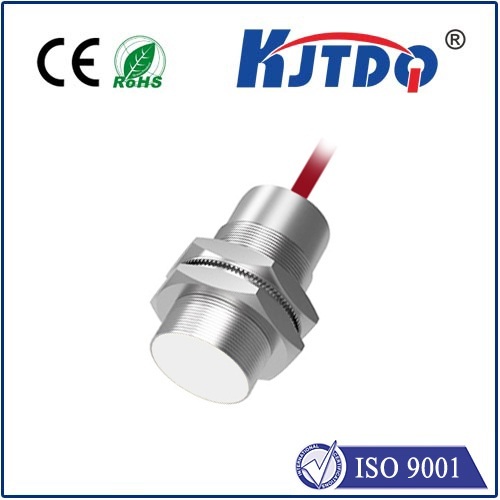
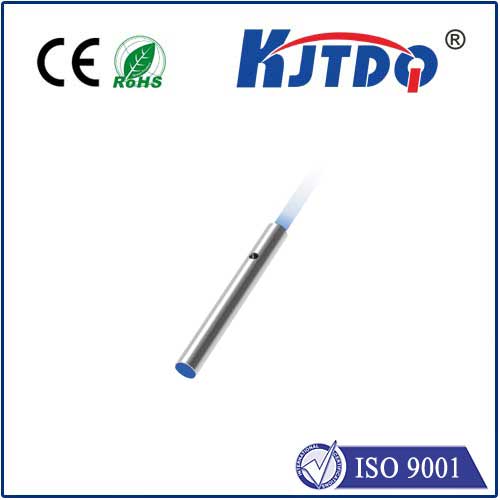
A proximity sensor is a non-contact device that uses electromagnetic fields to determine the proximity of an object to its sensor. In the context of metal detection, proximity sensors can be employed to detect the presence of metal objects within a particular range. By measuring the changes in electrical conductivity caused by the presence of metal particles, these sensors can identify the metal type and density with high accuracy and speed.
One of the major advantages of using proximity sensors for metal detection is their non-invasive nature. Unlike XRF analysis, which requires the extraction and analysis of samples from the production line, proximity sensors can operate in real-time, providing immediate alerts whenever metal objects are detected. This not only enhances safety but also minimizes downtime and reduces costs associated with sample preparation and analysis.
In addition to safety benefits, proximity sensors also offer significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy when compared to traditional metal detection techniques. By integrating these sensors into existing metallurgical processes, manufacturers can automate routine tasks, reduce human error, and optimize production workflows. For example, proximity sensors can be used to monitor the progress of material handling equipment, ensuring proper operation and preventing accidents caused by mishandling.
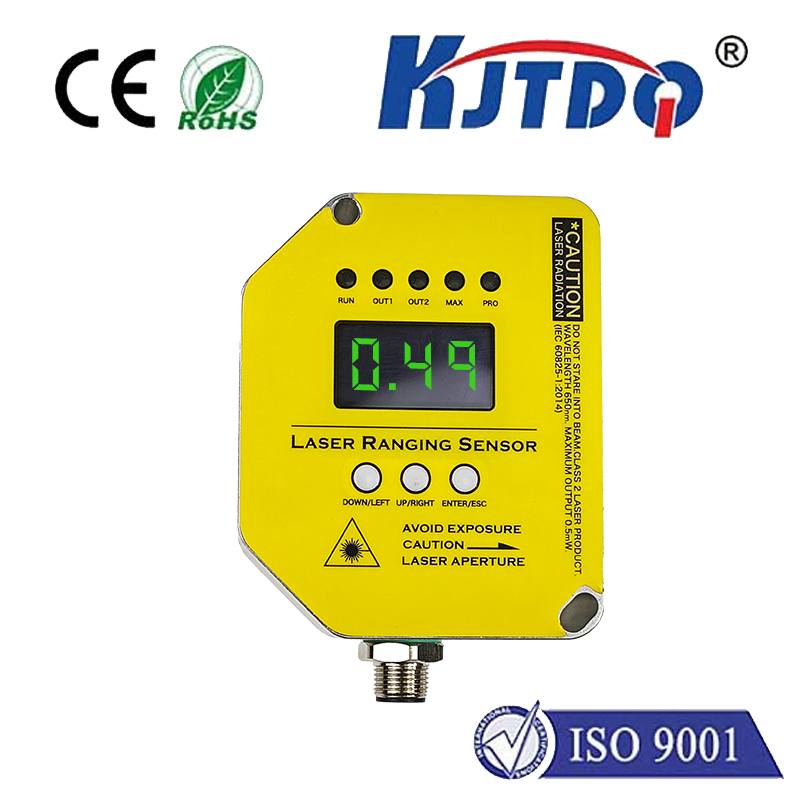
Moreover, proximity sensors enable real-time monitoring of metal concentrations in various stages of processing. By analyzing data collected by these sensors, metallurgists can gain insights into the behavior of metals during different stages of transformation, leading to improved product quality and process optimization. This information can also be used to identify potential sources of contamination and implement preventive measures to ensure consistent quality standards.
To achieve maximum efficiency and effectiveness in metal detection, it is essential to use high-quality proximity sensors that are designed for industrial environments. These sensors should be capable of detecting both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, as well as different types of alloys and composites. Additionally, they should have robust construction qualities and withstand harsh environmental conditions such as high temperatures, vibration, and moisture exposure.
In conclusion, proximity sensors have transformed the way metal detectors are used in the metallurgical industry. Their ability to detect metals accurately and instantly while minimizing costs and improving safety has made them a valuable tool for manufacturers looking to optimize their production processes. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advanced versions of proximity sensors that will provide further improvements in efficiency and accuracy in metal detection applications.