check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check

check
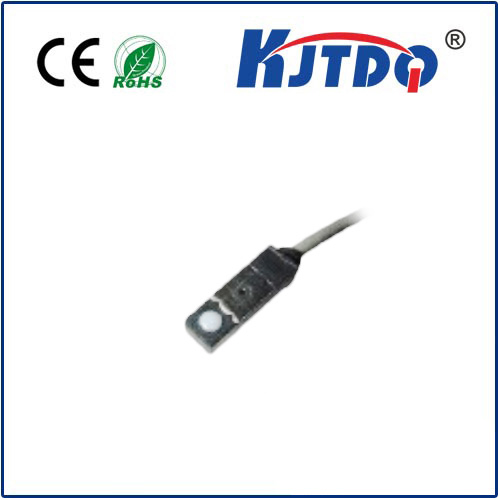
Inductive coil sensors are a type of transducer that uses a magnetic field to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They have a wide range of applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, industrial automation, and healthcare. In this article, we will provide an overview of inductive coil sensors, their working principle, advantages, and limitations.
The principle of operation of an inductive coil sensor involves the use of a magnetic field to create an electromotive force (EMF) in a coil of wire. When a current is applied to the coil, it generates a magnetic field that interacts with the external magnetic field. This interaction causes a voltage to be generated across the coil, which can be measured and converted into a physical signal.
One of the main advantages of inductive coil sensors is their simplicity and low cost. They require minimal maintenance and can operate reliably for extended periods without needing repairs or replacements. Additionally, they are non-contact sensors, making them ideal for detecting distances ranging from a few millimeters to several meters.
However, inductive coil sensors also have some limitations. They have a relatively low resolution, which means that they may not be able to detect small changes in the magnetic field. They are also susceptible to noise and interference from other sources, which can affect their accuracy and reliability. Furthermore, their response time can be slow, making them unsuitable for applications where rapid response is required.
Despite these limitations, inductive coil sensors continue to play an important role in various industries. They offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for detecting and measuring magnetic fields and have made significant contributions to advancements in technologies such as robotics, automation, and medical diagnosis. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that inductive coil sensors will continue to evolve and improve, providing even more advanced solutions for a variety of applications.